Chapter 1 Campbell Biology 11th Edition Vocabulary Flash Cards
1
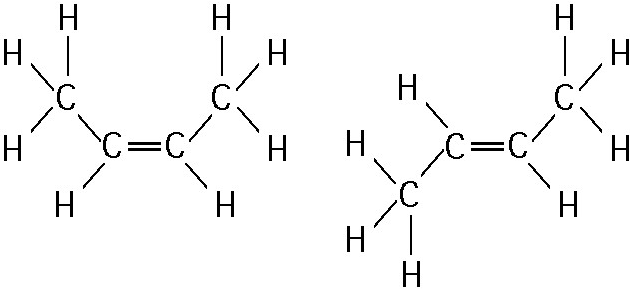
1) The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
A) Structural isomers.
B) Radioactive isotopes.
C) Enantiomers
D) Cis-trans isomers
2
2) Which of the following correctly describes any reaction that has reached chemical equilibrium?
A) All of the reactants have been converted to the products of the reaction
B) All of the products have been converted to the reactants of the reaction
C) Both the forward and the reverse reactions have stopped, with no net effect on the concentration of reactants and the products.
D) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
3
3) Which of the following statements is true about buffer solutions?
A) They maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them
B) They maintain a constant pH when acids are added to them but not when bases are added to them
C) They maintain a constant pH when bases are added to them but not when acids are added to them
D) They fluctuate in pH when either acids or bases are added to them
4
4) In living systems molecules involved in hydrogen bonding almost always contain either oxygen or nitrogen or both. How do you explain this phenomenon
A) Oxygen and nitrogen are elements found in fats and carbohydrates
B) Oxygen and nitrogen are elements found in both nucleic acids and proteins
C) Oxygen and nitrogen were both components of gases that made up the early atmosphere on Earth
D) Oxygen and nitrogen are elements with very attractions for their electrons
5
5) About twenty-five of the ninety-two natural elements known to be essential to life. Which four of these twenty-five elements make up approximately 96 percent of living matter?
A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen
B) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
C) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
D) carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium
6
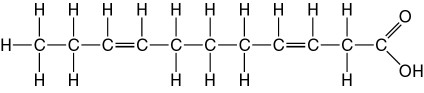
10) The molecule illustrated in the accompanying figure_____.
A) is a saturated fatty acid
B) will be liquid at room temperature
C) stores genetic information
D) is a carbohydrate
7
11) Which of the following is the strongest evidence that protein structure and function are correlated?
A) Enzymes tend to be globular in shape
B) Denatured (unfolded) proteins do not function normally
C) Proteins have four distinct levels of structure and many functions
D) Proteins function best at certain temperatures
8
12) What is the difference between covalent bonds and ionic bonds?
A) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms: ionic bonds involve the sharing of protons between charged atoms
B) Covalent bonds involve the transfer of electrons between charged atoms: ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms
C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms: ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms
D) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms: ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between charged atoms
9
13) Which of the functional groups below acts most like an acid in water?
A) Hydroxyl
B) Amino
C) Carboxyl
D) Carbonyl
10
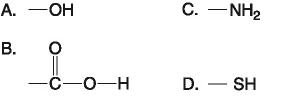
14) Which functional group shown above is a characteristic of alcohols?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
11
15) Which of the following includes all of the pyrimidines found in RNA and DNA?
A) Cytosine and thymine
B) Cytosine, uracil and guanine
C) Cytosine, uracil and thymine
D) Cytosine and uracil
12
16) Fluorine has an atomic number of 9. Which of the following would you do to a neutral fluorine atom to complete its valence shell?
A) Add 1 electron
B) Remove 1 electron
C) Add 2 electrons
D) Nothing. If fluorine is neutral, it has complete valance shell
13
17) The element present in all organic molecules is_____.
A) Hydrogen
B) Nitrogen
C) Carbon
D) Oxygen
14
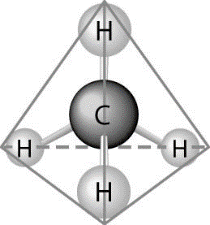
18) What causes the shape of the molecule shown above?
A) The shape of the sp3 hybrid orbitals of the electrons shared between the carbon and hydrogen atoms
B) The shape of the 1s orbital in the carbon atom
C) The shape of the 2p orbitals in the carbon atom
D) Hydrogen bonding configuration between the carbon and hydrogen atoms
15
19) Why is carbon so important in biology?
A) It bonds to only a few other elements
B) It has very little electronegativity, making it a good electron donor
C) It can form a variety of carbon skeletons and host functional groups
D) It is a common element on earth
16
20) Which of the following is NOT a polymer?
A) Starch
B) Cellulose
C) Glucose
D) DNA
17
21) Agrobacterium infects plants and causes them to form tumors. You determine that tumor formation requires a large amount of the plant's energy for tissue formation. How might this change the number of offspring a plant produces, and what is the most likely explanation for this change?
A) The number of offspring should increase, because in general, illness increases the reproductive output of organism
B) The number of offspring should increase, because the bacteria will provide energy for the plant
C) The should be no effect of infection on offspring production because energy for reproduction is independent of infection
D) The number of offspring should decrease, because the plant will divert energy from reproduction to tumor formation
18
22) A salamander relies on hydrogen bonding to stick to various surfaces. Therefore, a salamander would have the greatest difficulty clinging to a______.
A) Surface of hydrocarbons
B) Surface of mostly carbon-nitrogen bonds
C) Slightly damp surface
D) Surface of mostly carbon-oxygen bonds
19
23) Amino acids are acids because they always possess which functional group?
A) Carboxyl
B) Amino
C) Carbonyl
D) Phosphate
20
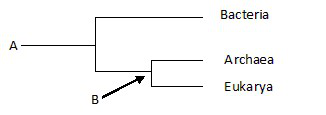
24) The phylogenetic tree below_____.
A) Includes noncellular life-forms
B) Depicts the three major domains of life
C) Includes unicellular and some of multicellular life, but not complex animals and plants
D) Includes unicellular but not multicellular life
21
25) A carbon atom is most likely to form what kind of bond(s) with other atoms?
A) Ionic
B) Hydrogen
C) Covalent
D) Ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds
22
26) Which of the following types of cells utilize deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as their genetic material but do not have their DNA encased within a nuclear envelope?
A) Archaean
B) Fungi
C) Animal
D) Plant
23
27) Why does ice float in liquid water?
A) The high surface tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top
B) The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water
C) Stable hydrogen bonds keep water molecules of ice farther apart than water molecules of liquid water
D) The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking
24
28) The molar mass of glucose is 180 grams per mole (g/mol). Which of the following procedures should you carry out make a 1 M solution of glucose? Into 0.8 liter (L) of water, dissolve____.
A) 18g of glucose and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1L
B) 180g of glucose and then add 0.2L more of water
C) 1g of glucose and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1L
D) 180g of glucose and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1L
25
29) How does a scientific theory differ from a scientific hypothesis?
A) Confirmed theories become scientific laws; hypotheses become theories
B) Theories are proposed to test scientific hypotheses
C) Theories are usually an explanation for a more general phenomenon; hypotheses typically address more specific issues
D) Hypotheses are usually an explanation for a more general phenomenon, theories typically address more specific issues
26
30) If a DNA sample were composed of 10% thymine, what would be the percentage of guanine?
A) 10
B) 40
C) 80
D) It is impossible to tell from the information given
27
31) The atomic number of chlorine is 17. The atomic number of magnesium is 12. What is the formula for magnesium chloride?
A) MgCl
B) Mg2Cl
C) MgCl2
D) MgCl3
28
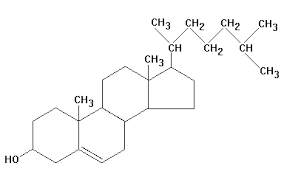
32) The molecule shown the accompanying figure is a _____.
A) Steroid
B) Protein
C) Fatty acid
D) Phospholipid
29
33) You find yourself standing next to a beautiful rose bush. Which of the following do you and the rose have in common?
A) You and the rose have nothing in common
B) You both are multicellular
C) You are both prokaryotic
D) You both lack a membrane-bound nucleus
30
34) The experimental approach taken in current biological investigations presumes that____.
A) A living organism can be understood in terms of the same physical and chemical laws that can be used to explain all natural phenomena
B) A life force ultimately controls the activities of living organisms and this force cannot be studied by physical or chemical bonds
C) Living organism are composed of the same elements present in nonliving things, plus a few special brace elements found only in living organism or their products
D) Simple organic compounds can be synthesized in the laboratory from inorganic precursors, but complete organic compounds like carbohydrates and proteins can be synthesized only by living organisms
31
35) Which level of protein structure do the a-helix and the B-pleated sheet represent?
A) Primary
B) Secondary
C) Tertiary
D) Quaternary
32
36) Increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations might have what effect on seawater?
A) There will be no change in the pH of seawater, because carbonate will turn to bicarbonate
B) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will decrease
C) Seawater will become more alkaline, and carbonate water concentrations will decrease
D) Seawater will become more acidic, and carbonate concentrations will increase
33
Use the following information when answering the corresponding question(s).
In 1668, Francesco Redi performed a series of experiments on spontaneous generation. He began by putting similar pieces of meat into eight identical jars. Four jars were left open to the air, and four were sealed. He then did the same experiment with one variation: Instead of sealing four of the jars completely, he covered them with gauze (the gauze excluded the flies while allowing the meat to be exposed to air). In both experiments, he monitored the jars and recorded whether or not maggots (young flies) appeared in the meat.
37) Refer to the paragraph on Redi's experiments. What hypotheses was being tested in the initial experiment with open versus sealed jars?
A) Spontaneous generations can occur only if meat is exposed to air
B) Spontaneous generations is more likely during the long days of summer
C) Maggots do not arise spontaneously, but from eggs laid by adult flies.
D) The type of meat used affects the likelihood of spontaneous generations
34
38) Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
A) The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages
B) The majority of their bonds are polar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages
C) They are less dense than water
D) They exhibit considerable molecular complexity and diversity
35
39) Which of these provides evidence of the common ancestry of all life?
A) Structure of cilia
B) Stricture of nucleus
C) Structure of chloroplasts
D) Near universality of the genetic code
36
40) Which polysaccharide is an important component in the structure of many animals and fungi?
A) Cellulose
B) Amylose
C) Amylopectin
D) Chitin
37
41) Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
A) Hydrogen bonds
B) Both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
C) Polar covalent bonds
D) Ionic bonds
38
42) If the cytoplasm of a cell is at pH 7, and the mitochondrial matrix is at pH 8, then the concentration of H+ ions_______.
A) In the cytoplasm is 8/7 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix
B) Is 10 times higher in the cytoplasm than in the mitochondrial matrix
C) In the cytoplasm is 7/8 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix
D) Is 10 times higher in the mitochondrial matrix than in the cytoplasm
39
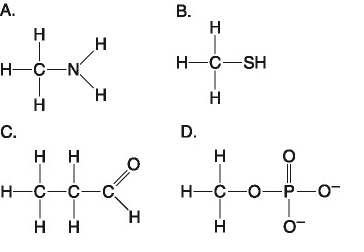
43) Which molecule shown above contains an amino acid functional group, but is NOT an amino acid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
40
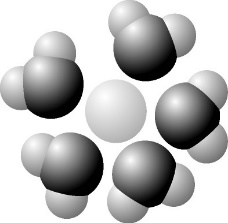
44) Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule depicted here is most likely_______.
A) Nonpolar
B) Negatively charged
C) Without charge
D) Positively charged
41
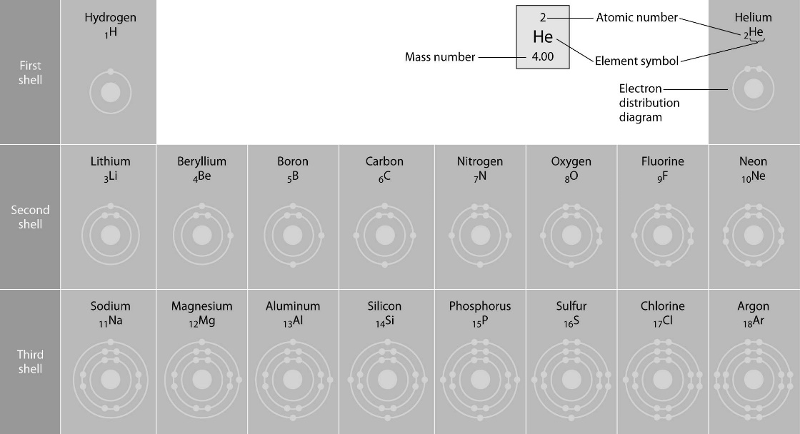
45) Refer to the figure above (first three rows of the periodic table). What element has properties most similar to carbon?
A) Silicon
B) Boron
C) Nitrogen
D) Phosphorus
42
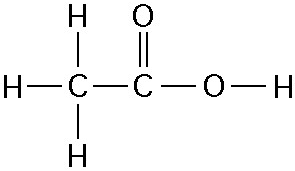
46) One mole of the compound above would weigh how many grams? (Note: The atomic masses, in daltons, are approximately 12 for carbon, 1 for hydrogen, and 16 for oxygen.)
A) 29
B) 150
C) 60
D) 30
43
47) Normal hemoglobin is a tetramer, consisting of two molecules of B hemoglobin and two molecules of a hemoglobin. In sickle-cell disease, as a result of a single amino acid change, the mutant hemoglobin tetramers associate with each other and assemble into large fibers. Based on this information alone, we can conclude that sickle-cell hemoglobin exhibits______.
A) Only altered primary structure
B) Only altered tertiary structure
C) Only altered quaternary structure
D) Altered primary structure and altered quaternary structure; the secondary and tertiary structures may or may not be altered
44
48) A controlled experiment_______.
A) Includes at least two groups, one differing from the other by two or more variables.
B) Includes one group for which the scientist controls all variables
C) Is repeated many times to ensure that the results are accurate
D) Includes at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment
45
49) Which of these is an example of inductive reasoning?
A) These organism live in sunny regions. Therefore, they are using photosynthesis
B) In two species are members of the same genus, they are more alike than each of them could be to a different genus
C) Hundreds of individuals of a species have been observed and all are photosynthetic; therefore species is photosynthetic
D) If protists are all single-celled, then they are incapable of aggregating
46
50) Hydrophobic substance such as vegetable oil are_____.
A) Nonpolar substance that have attraction for water molecules
B) Polar substances that repel water molecules
C) Polar substances that have an affinity for water
D) Nonpolar substance that repel water molecules
Chapter 1 Campbell Biology 11th Edition Vocabulary Flash Cards
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/41480
0 Response to "Chapter 1 Campbell Biology 11th Edition Vocabulary Flash Cards"
Post a Comment